Deciding Between 2D and 3D Graphs: Which One Should You Choose?
Deciding between a 2D and 3D graph can sometimes feel like choosing the right tool from an overstocked toolbox—there are many options, and it’s not always clear which one will get the job done successfully. Should you keep it simple with a 2D graph, or go bold with the depth and dimension of 3D? While the decision might seem tricky at first, making the right one is far from impossible. In fact, you can confidently choose the format that best suits your data-driven story; and the road to doing so is quite easy.
2D and 3D Graphs: A Quick Overview
Before we dive in, let’s quickly define 2D and 3D graphs. A 2D graph illustrates values from one or more variables on a flat, two-dimensional plane, while a 3D graph takes it a step further, adding depth to display values in three dimensions.
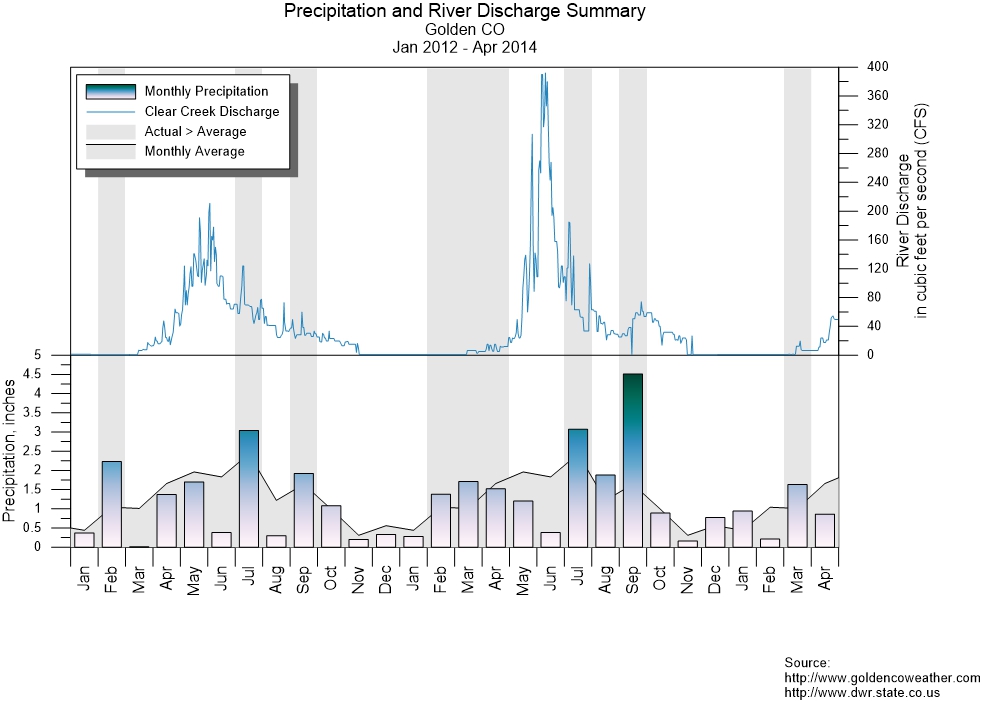
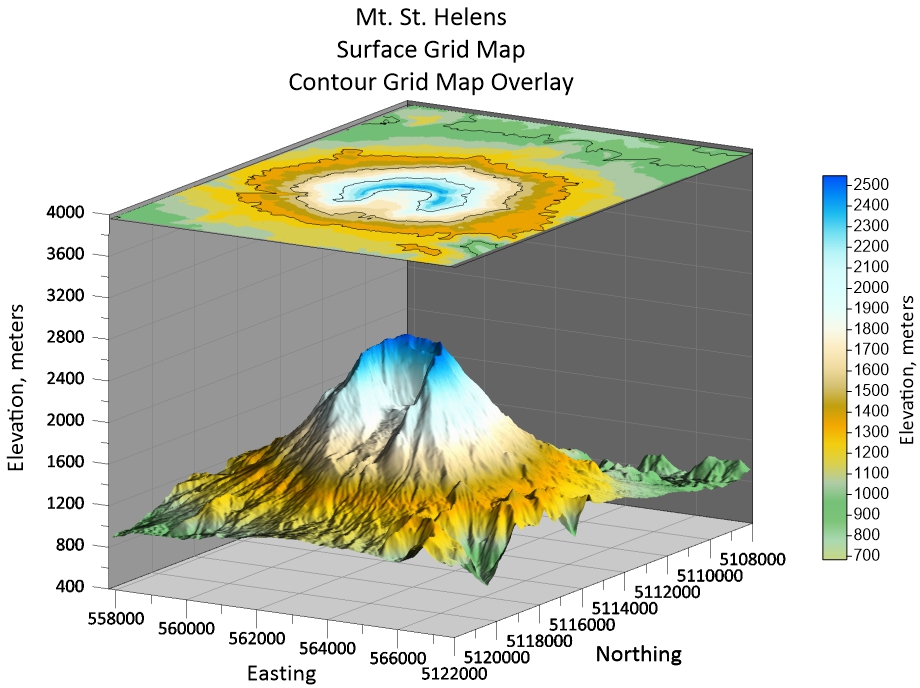
Both formats offer a variety of options, from familiar bar charts and histograms to more complex visuals like class scatter plots. Some graphs, however, are exclusive to their format—hydrographs are usually 2D, while surface data maps belong to the 3D world.
The challenge arises when a graph can exist in either format. In those cases, you have to determine which format is best, and the first step in making that decision is understanding that 2D and 3D graphs are most effective in different situations.
When to Use 2D Graphs
Now, it’s time to answer a critical question: in what cases are 2D graphs the best visual for your data? To be honest, 2D visualizations are incredibly versatile and effective at representing complex information, so you can use them in almost any situation. However, there are three key scenarios where these types of graphs excel.
1. Comparing Two Variables
2D graphs are ideal for showing relationships between two variables. For instance, a scatter plot can reveal the correlation between soil salinity and crop yield in agricultural studies, while a line graph can track the change in a chemical compound’s reactivity under varying temperatures.
2. Displaying Time-Series Data
When you need to showcase changes over time, 2D graphs—like line or bar charts—are incredibly effective. For example, a 2D line graph can illustrate fluctuations in atmospheric CO₂ levels over decades, while a bar chart can show annual rainfall totals for a specific region. In both scenarios, you can easily pinpoint to stakeholders key events or anomalies in your data.
3. Ensuring Simplicity and Accessibility
If your audience includes non-experts or stakeholders less familiar with your complex data, a 2D graph can be helpful. Its straightforward design makes it accessible and easy to interpret. For instance, a bar graph comparing energy output across renewable sources requires minimal explanation and is understood by a wide range of viewers.
When to Use 3D Graphs
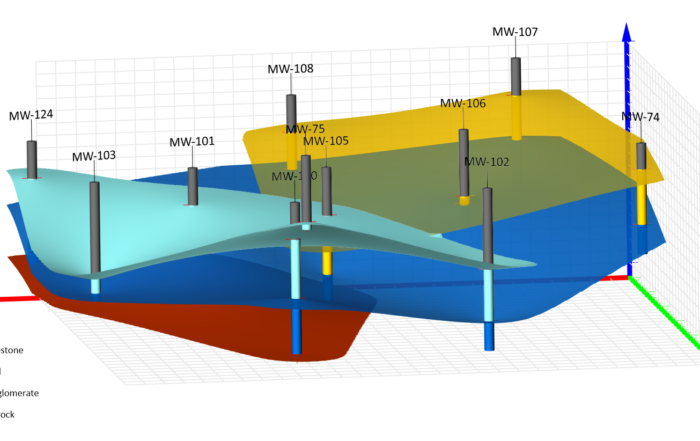
While 2D graphs are versatile, there’s one key scenario where 3D visuals truly shine: when you need to show the relationship between three variables. In this case, the third dimension adds valuable depth to your data, equipping stakeholders to see how multiple variables interact in a way that 2D graphs can’t effectively show.
Consider this: maybe you’re studying the effects of temperature, pressure, and time on a chemical reaction. A 3D surface map can equip you to visualize the interplay between these three variables, revealing how different combinations produce varying reaction rates. With the peaks, valleys, and slopes shown three-dimensionally, you can convey critical insights to help stakeholders determine the optimal conditions for the reaction.
Still, despite their strengths, 3D graphs come with challenges. While they can show the relationship between multiple variables, they’re still harder to interpret, especially for non-technical audiences, as perspective and overlapping elements may obscure key insights. That’s why it’s essential to apply data visualization best practices when creating 3D graphs. A few quick tips you can implement are the following:
- Keep your designs clean and clutter-free
- Use color gradients effectively to highlight patterns
- Spotlight major points to keep your audience focused on what really matters
- Provide clear labels so your audience can engage with your visualization without confusion
When used appropriately and thoughtfully, 3D graphs can be powerful tools for conveying complex relationships. But clarity is critical—your goal should always be to make your data clear, accurate, and visually compelling.
The Situation Matters
Ultimately, both 2D and 3D graphs have their strengths, but their true potential shines in specific situations. If you’re wondering whether to use a 2D or 3D graph, focus on what you’re trying to achieve, and let that guide your choice. Once you’ve made your decision, you can dive into creating your graph—and if you need a hand, try Grapher. With a 14-day free trial, you’ll have access to a range of features and customization tools to ensure your visualization truly wows stakeholders.